Treatment Options
Conservative Treatment
For an arteriovenous malformation (AVM), conservative treatment typically involves managing symptoms and monitoring the condition without immediate intervention through surgery or other invasive procedures. The primary goals of conservative treatment are to alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. This approach may include medication to control seizures, pain, or other symptoms, regular imaging to monitor the AVM’s size and any changes, and lifestyle adjustments to minimize strain on the cardiovascular system. Conservative management is usually recommended for smaller AVMs that are not causing significant health issues or if the risks of surgery or other invasive treatments outweigh the potential benefits. Close monitoring by a healthcare professional is essential to determine if and when more aggressive treatment might become necessary.
Surgery
Surgical treatment for an arteriovenous malformation (AVM) involves the removal or repair of the AVM through a surgical procedure, often with the goal of preventing complications like bleeding or seizures. The most common surgical approach is direct resection, where the AVM is carefully removed from the brain or affected area. This is typically done when the AVM is accessible and located in a region where surgery poses manageable risks. Another surgical option is endovascular embolization, where a catheter is used to block the blood vessels feeding the AVM, shrinking or eliminating the malformation. In some cases, a combination of surgery, embolization, and/or radiation therapy (stereotactic radiosurgery) may be used to treat the AVM effectively. Surgical options depend on factors such as the AVM’s size, location, and the patient’s overall health, and are determined after a thorough evaluation by a specialist.
Endovascular Treatment
Endovascular treatment for an arteriovenous malformation (AVM) involves using a catheter inserted into a blood vessel to deliver targeted treatments directly to the AVM. One common approach is endovascular embolization, where the catheter is guided to the AVM’s feeding arteries, and a special substance (such as coils, glue, or a liquid embolic agent) is injected to block blood flow to the malformation. This can help shrink or eliminate the AVM, reducing the risk of bleeding or other complications. Endovascular treatments are often used as a primary treatment for certain AVMs or as part of a combination therapy, sometimes alongside surgery or radiosurgery. This minimally invasive procedure offers a less invasive alternative to traditional surgery and is particularly beneficial for AVMs located in areas that are difficult to reach surgically. However, the decision to use endovascular treatment depends on the size, location, and characteristics of the AVM, as well as the patient’s individual health situation.
Hybrid treatment
for an arteriovenous malformation (AVM) combines multiple therapeutic approaches, such as endovascular embolization, surgical resection, and sometimes radiosurgery, to achieve the most effective outcome. This multi-faceted approach is often used when an AVM is complex, large, or located in a challenging area where a single treatment may not be sufficient. For example, endovascular embolization may first be used to reduce the size of the AVM and make surgical resection safer and easier, or it may be combined with stereotactic radiosurgery to target residual AVM tissue after surgery. Hybrid treatments allow for a tailored approach that addresses the AVM’s unique characteristics while minimizing risks and improving the likelihood of successful treatment. This approach is typically considered for AVMs that cannot be effectively treated by one method alone, and decisions are made based on the AVM’s size, location, and the patient’s overall health.

Case Presentation
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry’s standard dummy text ever since the 1500s, when an unknown printer took a galley of type and scrambled it to make a type specimen book. It has survived not only five centuries, but also the leap into electronic typesetting, remaining essentially unchanged. It was popularised in the 1960s with the release of Letraset sheets containing Lorem Ipsum passages, and more recently with desktop publishing software like Aldus PageMaker including versions of Lorem Ipsum.Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry’s standard dummy text ever since the 1500s, when an unknown printer took a galley of type and scrambled it to make a type specimen book. It has survived not only five centuries, but also the leap into electronic typesetting, remaining essentially unchanged.
PATIENT SUPPORT

Education:
At our center, patient support goes beyond treatment—we are committed to educating and empowering patients and their families about arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) and related vascular conditions. Through our website and educational programs, we aim to raise awareness and provide valuable information about the challenges associated with AVMs. We believe that informed patients are better equipped to make decisions about their care. Additionally, we collaborate with the Indian Society of Vascular Anomalies (ISVA) to further promote public awareness and share the latest research, treatment options, and expert insights. Our goal is to foster a supportive community, helping individuals affected by AVMs navigate their journey with confidence, while also educating the broader public about the importance of early detection, diagnosis, and treatment of vascular anomalies.

Support:
Our goal is to create a strong, supportive community for individuals affected by arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). We understand that facing an AVM diagnosis can be overwhelming, which is why we are working to establish a dedicated support group where patients and their families can connect, share experiences, and learn from one another. By joining this group, individuals will have the opportunity to raise awareness, discuss treatment options, and provide emotional support to others facing similar challenges. Through shared knowledge and personal stories, we aim to empower each member and help spread awareness about AVMs to the broader public. Together, we can create a network of understanding, reduce stigma, and ensure that no one has to face the journey of living with an AVM alone.
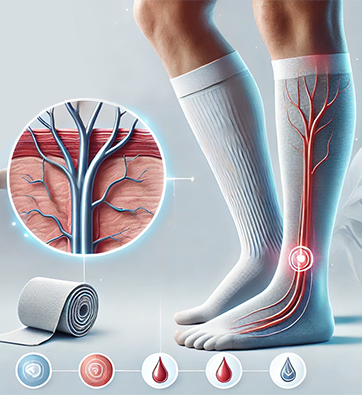
Compression - Stocking and Wraps:
Compression stockings and wraps play a crucial role in managing the symptoms of arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), particularly when the condition affects the veins or causes swelling. These garments help promote better blood circulation by applying consistent pressure to the affected area, which can reduce swelling, prevent blood pooling, and alleviate discomfort. For AVM patients, compression therapy can help manage varicose veins, improve venous return, and reduce the risk of complications such as deep vein thrombosis or further vascular damage. Wearing compression stockings or wraps as recommended by healthcare professionals is an effective, non-invasive way to support the vascular system, enhance comfort, and improve overall quality of life. Regular use can also help maintain skin integrity and prevent further deterioration in areas with compromised blood flow.
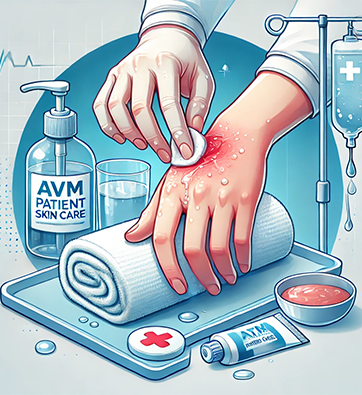
Skin Care:
For AVM patients, especially those with wounds or areas of skin affected by the condition, maintaining proper skin care is essential to prevent infections, promote healing, and manage discomfort. It’s important to keep the wound area clean and dry by gently washing it with mild soap and water, avoiding harsh chemicals or scrubbing, which could irritate the skin. Applying a sterile dressing to the wound, as recommended by a healthcare provider, can help protect it from bacteria and keep the area moist, which aids in healing. Regularly inspecting the skin for signs of redness, swelling, or infection is crucial, as AVM-related wounds may be more prone to complications. Moisturizing the surrounding skin with non-irritating lotions or creams can also prevent dryness and cracking, which can further disrupt healing. Patients should avoid tight clothing or compression garments that may rub against the wound area, and always follow their doctor’s specific instructions on wound care. Proper skin care helps reduce the risk of complications and supports the healing process, contributing to the overall well-being of AVM patients.

Genetics:
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) that occur due to genetic factors are often the result of inherited mutations that affect the normal development of blood vessels. In some cases, these genetic changes disrupt the formation of arteries and veins, causing them to form abnormal connections. These malformations can be present from birth and may be linked to specific genetic conditions, such as hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) or other vascular syndromes. Genes control the development of blood vessels, and when mutations occur in these genes, they can lead to the formation of AVMs. These faulty genetic instructions prevent the blood vessels from forming correctly, resulting in tangled, weak connections between arteries and veins that bypass normal capillary networks. This leads to issues with blood flow and increases the risk of bleeding or other complications. While genetic mutations are not the only cause of AVMs, they significantly increase the likelihood of their development in newborns, making early monitoring and genetic counseling important for managing these conditions.
